
LEO SATELLITES AT WORK
alleviating global food insecurity
Digital technologies and broadband internet are revolutionizing farming and agricultural practices—from connected sensors that monitor crop yields, microclimates, storage facilities or livestock to precision seeding and autonomous vehicles. But these promising advances are being held back by insufficient rural broadband access.
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites provide another option to bring fast, affordable and reliable broadband to rural areas that are underserved by other technologies and enable connectivity across and even enable connectivity across expansive lands and large properties. Connectivity empowers farmers and producers with the 21st-century tools and efficiencies they need to thrive and alleviate global food shortages.

Case Study: Farming
In rural regions, LEOs’ impact on agricultural efficiencies is helping change the game in farming. Jacquelyne Leffler, who runs Leffler Farms in rural Kansas, said, “[B]efore Starlink, it was faster for me to download our farm data to a flash drive and mail it … Starlink has been incredible in helping us stay connected to the world – even if we are rural.”
Case Study: Food Insecurity
Togo faced exacerbated food insecurity due to COVID-19 supply chain disruptions. A collaboration involving NASA Harvest, Planet Labs and the University of Maryland utilized LEO satellite technology to address this crisis. By leveraging high-resolution satellite imagery and advanced analytics, Togo authorities could make informed decisions about resource allocation and distribution, effectively mitigating the impact of the pandemic on food security.
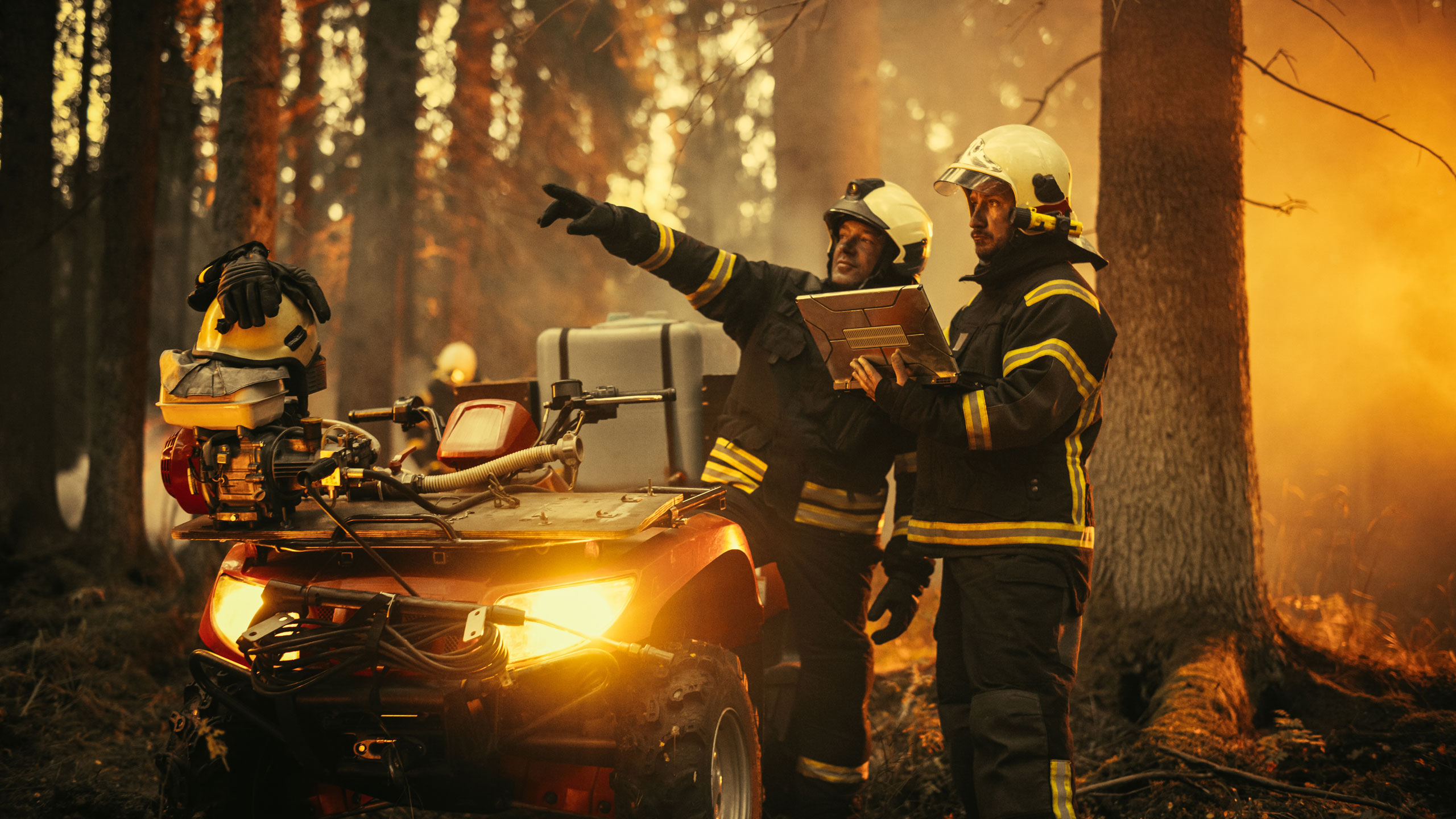
Staying Connected in Crisis
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite technology is a critical tool to save lives and keep us connected during crises. Because LEO satellites are less dependent on terrestrial infrastructure, they can provide ongoing connectivity during natural disasters — times when maintaining communication is especially critical and when other broadband technologies can often fail. LEO technologies empower first responders, healthcare facilities and other key institutions to stay online and connected globally, even in hard-to-reach areas or when on the move.

Case Study: Hurricane Helene
In September 2024, Hurricane Helene stormed the Southeast Coast and hit North Carolina especially hard. Traditional broadband and cell service went offline for days — and in some places, for weeks. But LEOs were there to help. Using LEO satellite technology, Maggie Watkins, a resident of rural Swannanoa, North Carolina was able to stay connected and confirm that her family was okay after the storm.
Case Study: Myanmar Earthquake
In March, India deployed internet connectivity provided by low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites for the first time to support emergency relief efforts. LEO connectivity allowed the teams in Myanmar to remain online and in communication throughout recovery operations.
Internet on the Go
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites provide fast, affordable broadband access — anywhere. LEO satellites are also making the world of travel safer by keeping people connected to GPS and emergency services. This includes places and applications where high-speed internet has previously been spotty, unreliable or unavailable.

Case Study: 2024 Baja 1000
In the 2024 Baja 1000, an off-road bike race on the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico, Ben Hundter, a diabetic racer, raced with a LEO satellite terminal duct taped to his helmet so his mom could ride along and monitor his condition. Hundter said, “I wanted to race the Baja so bad, but my mom wouldn’t let me because I have type 1 diabetes. She said the only way I could race it is if I was live streaming to her the whole time, so I have her on my chest right now.” He finished second in class.
Bridging the Digital Divide
Emphasizing the role of every connectivity technology, including LEO technology, in connectivity portfolios can give everyone, everywhere, the opportunity to access fast, affordable broadband — including regions and communities across the world where it is unfeasible or impossible to extend other technologies due to geographic barriers or economic factors. LEO satellites have the potential to play a pivotal role in helping to close the digital divide by providing a new, reliable and cost-effective broadband option to previously underserved or unserved areas.
Case Study: Education
In 2022, the Southeast Island District, a small school district in rural Alaska, saw an opportunity to slash costs and improve connectivity for the district by switching to LEO satellite internet. Today, Everett Cook, the district’s technology director, says the switch has resulted in “just a phenomenal increase. I haven’t heard anything about slow internet anymore … It’s affordable, it works really great, and parent communication is increasing because of it.”
Case Study: Telehealth
Reliable, high-speed internet from LEO satellites is transforming telehealth in rural Southwest Virginia by making telemedicine services accessible for underserved and remote communities, unlocking game-changing mobile health applications for virtual consultations, disease management and dedicated and timely patient care for anyone, anywhere.
